- Fitness (19)
- News & Reviews (25)
- Nutrition (20)
- Science (10)
- Supplements (6)
- Technologies (8)
- The Arts (9)
Never Go To Bed Angry
February 4th, 2012
 By Anahad O’Connor, the New York Times: Most people have heard the old saw about going to bed upset: Never do it, the saying goes, or the hard feelings will fester and resentment will build.
By Anahad O’Connor, the New York Times: Most people have heard the old saw about going to bed upset: Never do it, the saying goes, or the hard feelings will fester and resentment will build.Some say it goes back to the Bible, in Ephesians 4:26. “Let not the sun go down upon your wrath.” Regardless of its origins, the adage has been scarcely researched. But in a recent study in The Journal of Neuroscience, scientists found there might be a nugget of truth to it: Going to sleep after experiencing negative emotions appears to reinforce or “preserve” them.
Filed under Science | Comments Off on Never Go To Bed AngryWhat ‘They’ Said
October 25th, 2011

More at ‘The Week’
The Art of Science
August 20th, 2011

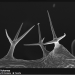
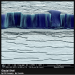
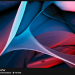
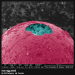
FEI produces and distributes electron microscopes for nanoscale research. They hold an annual image contest among those who own their machines and exhibit these images on their site. The 2011 winner (above) by Martina Dienstleder (hand-colored by Manuel Paller) is a micrograph of a cracked particle of steel.
Here are a few more images from their gallery:
Filed under Science | Comments Off on The Art of ScienceBuilding Smarter Beings
July 17th, 2011
 By Riddhi Shah of the HuffingtonPost: Over the last decade, interest in the science of meditation has skyrocketed. We now know more than ever before about just how meditation affects our minds and bodies. Increased research has led to a plethora of fascinating discoveries: Take, for instance, the fact that meditation can prevent heart disease. Or that it reduces stress. Or that it can significantly lessen ADHD symptoms, and in many cases, beats medication.
By Riddhi Shah of the HuffingtonPost: Over the last decade, interest in the science of meditation has skyrocketed. We now know more than ever before about just how meditation affects our minds and bodies. Increased research has led to a plethora of fascinating discoveries: Take, for instance, the fact that meditation can prevent heart disease. Or that it reduces stress. Or that it can significantly lessen ADHD symptoms, and in many cases, beats medication.
Still, much is left to be discovered. We know more but we definitely don’t know everything. While we wait for science to catch up with ancient wisdom, check out this slideshow on the complex effects of the simple act of focused breathing [here are its salient points]:
- [S]ustained meditation leads to something called neuroplasticity, which is defined as the brain’s ability to change, structurally and functionally, on the basis of environmental input. For much of the last century, scientists believed that the brain essentially stopped changing after adulthood. But research by University of Wisconsin neuroscientist Richard Davidson has shown that experienced meditators exhibit high levels of gamma ray activity and display an ability — continuing after the meditation session has attended — to not get stuck on a particular stimulus. That is, they’re automatically able to control their thoughts and reactiveness.
Meditation For ADHD Teens & Adults
May 1st, 2011
 Mindfulness meditation significantly helped three-quarters of the participants in a study described here by Dr. David Rabiner: Because of the wide spread interest in new ADHD interventions — particularly non-pharmaceutical approaches — I try to cover credible research in this area when ever I come across it. I was thus pleased to learn about a very interesting study of mindfulness meditation as a treatment for adults and adolescents with ADHD that was published in the Journal of Attention Disorders.
Mindfulness meditation significantly helped three-quarters of the participants in a study described here by Dr. David Rabiner: Because of the wide spread interest in new ADHD interventions — particularly non-pharmaceutical approaches — I try to cover credible research in this area when ever I come across it. I was thus pleased to learn about a very interesting study of mindfulness meditation as a treatment for adults and adolescents with ADHD that was published in the Journal of Attention Disorders.
Although medication treatment is effective for many individuals with ADHD, including adolescents and adults, there remains an understandable need to explore and develop interventions that can complement or even substitute for medication. (…)
In recent years, mindfulness meditation has been used as a new approach for stress reduction and incorporated into the treatment for a variety of psychiatric disorders, including depression, anxiety, and substance abuse. Of special relevance to the treatment of ADHD are findings that meditation has the potential to regulate brain functioning and attention. For example, research has demonstrated that mindfulness meditation can modify attentional networks, modulate EEG patterns, alter dopamine levels, and change neural activity.
Filed under News & Reviews | Comments Off on Meditation For ADHD Teens & Adults